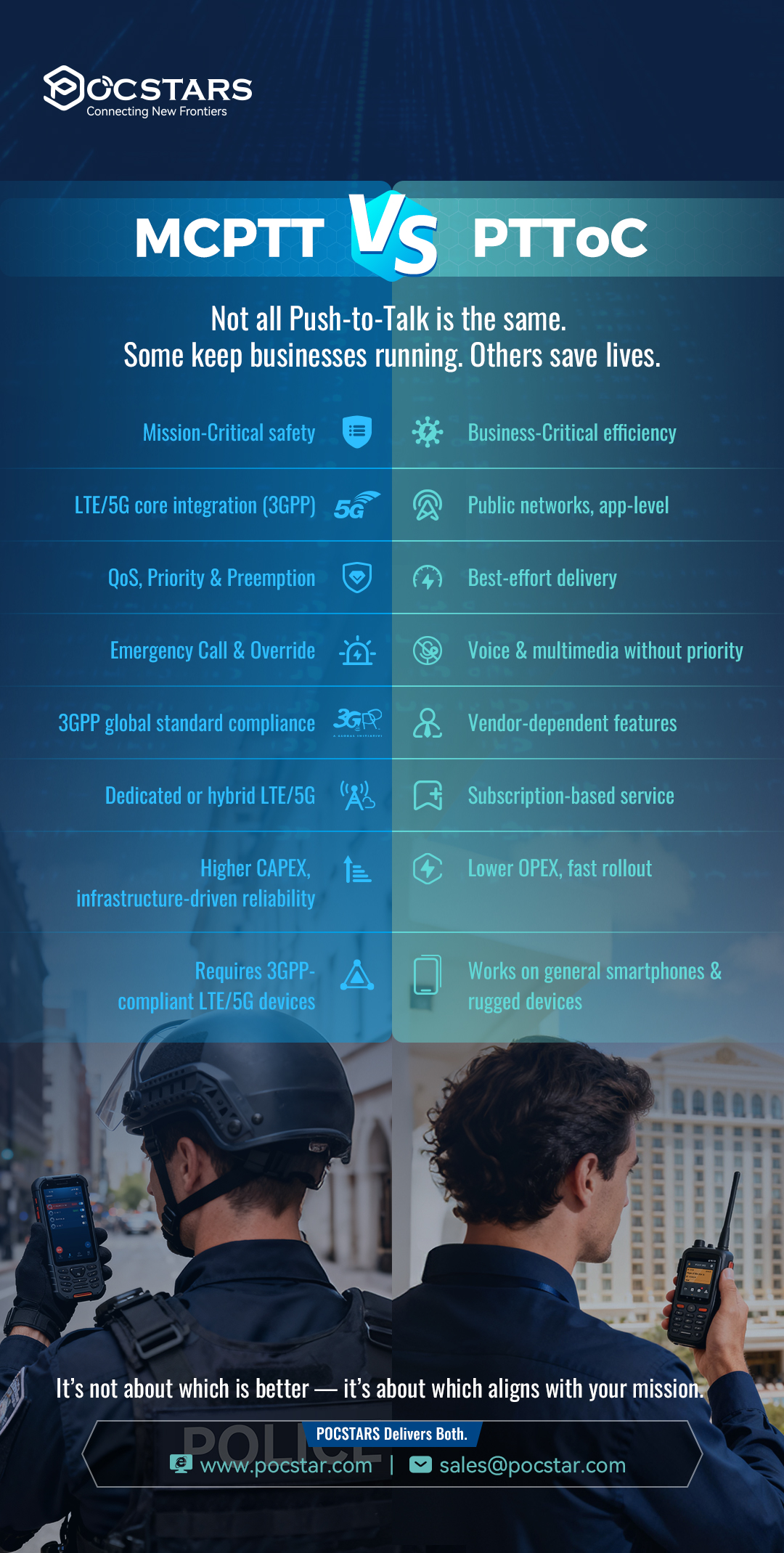
MCPTT and PTToC both deliver push-to-talk over cellular networks — but they serve very different missions.
MCPTT is a 3GPP-defined mission-critical service built around priority, preemption, and emergency functions.PTToC (often referred to as PoC / PTT over Cellular) is typically a business-critical platform designed for fast rollout and cost efficiency on public networks.
If you are evaluating push-to-talk for public safety or enterprise operations, this article explains the difference, what each model is designed for, and how to choose based on mission requirements.
Exploring MCX capabilities beyond MCPTT?
View the MCX Solution PageMCPTT vs PTToC: Key Differences, Standards, and When to Use Each
TL;DR — when to choose MCPTT vs PTToC
Choose MCPTT when communications must be protected under congestion and emergency workflows are required (e.g., public safety, emergency response, defence).
Choose PTToC / PoC when operational efficiency and rapid deployment matter most (e.g., logistics, private security, enterprise operations).
What is MCPTT?
MCPTT stands for Mission Critical Push-to-Talk, a standard defined by 3GPP (Release 13). It is part of the 3GPP mission-critical services family, often referred to as MCX.
Unlike ordinary commercial PTT apps, MCPTT introduces mission-critical mechanisms such as:
QoS, Priority & Preemption — to protect critical communications under congestion
Emergency Call & Override — to enable urgent access when seconds matter
Interworking with LMR systems — bridging legacy radio workflows with broadband networks
Security mechanisms — supporting protected communications end-to-end
In short: MCPTT is not just “better PTT” — it is mission-critical by design.
MCPTT vs PTToC: two models, two missions
While both deliver push-to-talk over broadband, MCPTT and PTToC differ in purpose, network integration, feature sets, cost models, and device requirements.
Key differences at a glance
Standardisation: MCPTT follows 3GPP specifications; PTToC feature sets vary by platform/vendor.
Service assurance: MCPTT is designed around priority/preemption mechanisms; PTToC is typically best-effort on public networks.
Emergency workflows: MCPTT supports emergency functions; PTToC often does not support these at network level.
Deployment model: MCPTT is often deployed with dedicated or hybrid LTE/5G; PTToC commonly rolls out as a subscription/OPEX service.
Devices: MCPTT requires 3GPP-compliant LTE/5G terminals; PTToC runs on general smartphones and rugged devices.
Extended explanation
1) Network architecture
PTToC / PoC: Runs as an application/service over public LTE/4G/5G networks.
MCPTT: Designed for LTE/5G core integration using 3GPP-defined interfaces.
2) Service quality
PTToC / PoC: Best-effort delivery, subject to congestion.
MCPTT: Built around mechanisms such as QoS, priority and preemption to protect critical calls under load.
3) Features
PTToC / PoC: Group/individual voice and basic dispatch features; multimedia depends on platform.
MCPTT: Adds mission-critical functions such as emergency call and override, and aligns with the broader evolution
toward services like MCData/MCVideo within the MCX family.
4) Standards
PTToC / PoC: Feature sets vary by vendor/platform.
MCPTT: Aligned with global 3GPP standards, enabling more consistent interoperability expectations in mission-critical ecosystems.
5) Deployment & cost models
PTToC / PoC: Subscription-based, OPEX-driven, rapid rollout, lower per-user cost.
MCPTT: Often involves higher upfront investment to meet mission-driven requirements.
6) Device requirements
PTToC / PoC: Works on general-purpose smartphones and rugged devices.
MCPTT: Requires 3GPP-compliant LTE/5G terminals to enable mission-critical mechanisms.
Where does PoC fit?
PTToC is commonly positioned as a PoC (Push-to-Talk over Cellular) approach for enterprise and operator-driven service models. For operator-facing PoC delivery and operating models, you may also find this useful:POCSTARS MNO solution.
Looking into PoC platforms and rollout options?
View the PoC / MNO Solution PageFAQ
Is MCPTT the same as MCX?
MCPTT is a mission-critical push-to-talk service within the broader 3GPP mission-critical services family (MCX).
Is PTToC always “non-critical”?
PTToC is often used for business-critical operations where speed, scalability and cost efficiency are priorities. The level of service assurance depends on the platform and network conditions.
Which one should I choose?
If priority under congestion and emergency workflows are mandatory, MCPTT is typically the reference approach. If rapid rollout and cost efficiency are the primary goals, PTToC/PoC is often the practical starting point.
Conclusion
Both PTToC and MCPTT are valuable — but for different missions.
PTToC / PoC supports flexible, cost-effective push-to-talk for enterprise operations.
MCPTT aligns with 3GPP mission-critical requirements around priority, emergency functions and standardisation.
POCSTARS provides solutions across both business-critical and mission-critical scenarios. If you are evaluating MCPTT or PoC/PTToC, share your deployment context and requirements — and we can help map the right approach.
Related reading
MCPTT ≠ PMR/LMR: Understanding the Evolution of Mission-Critical Communications
Last updated: 2026-01-06